Scientific research is a structured intellectual process that solves problems in an organized scientific way, and it is crucial in times of crises and disasters. It involves six steps: purpose, research, hypothesis, experiment, data analysis, and conclusion.
Scientific research is important as it contributes to the development and improvement in all fields, helps in solving problems that affect society, and has led to advancements in various fields such as medicine and communication. The future of scientific research is promising, with the development of new technologies and techniques that allow for deeper exploration and understanding of the natural world.
The main characteristic of scientific research is empirical research, which is based on observable and measurable evidence, and engages with the material world.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
What Is Scientific Research?
Introduction paragraph about Basics Of Scientific Research: What, How, And All About and What is Scientific Research? Scientific research is a systematic and methodical investigation to find solutions to problems, answer questions, or discover new knowledge. It involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data to answer specific questions or test hypotheses. Scientific research is a critical aspect of advancing knowledge and understanding in various fields.
Definition Of Scientific Research
Scientific research can be defined as a systematic and organized study to explore, interpret, and understand the world around us. It involves formulating a hypothesis, conducting experiments or observations, and analyzing data to draw conclusions. The process is characterized by objectivity, precision, and critical evaluation of evidence. Scientific research aims to expand our knowledge base, solve practical problems, and contribute to the development of new technologies and innovations.
Importance Of Scientific Research
Scientific research holds immense significance in various aspects of human life and society. Some key reasons for its importance include:
- Advancing knowledge and understanding in diverse fields
- Contributing to technological and medical advancements
- Solving practical problems and addressing societal challenges
- Supporting evidence-based decision making in policy and governance
- Fostering innovation and creativity
- Driving economic and social progress
These aspects collectively emphasize the critical role of scientific research in shaping the present and future of humanity.

Credit: sitn.hms.harvard.edu
Types Of Scientific Research
When it comes to scientific research, it can be broadly categorized into different types, each serving a unique purpose in the pursuit of knowledge and understanding. Understanding the various types of scientific research is crucial for researchers and scholars to choose the most suitable approach for their studies. Let’s delve into the different types of scientific research to gain insights into their characteristics and applications.
Basic Research
Basic research, also known as pure or fundamental research, aims to expand our understanding of fundamental scientific principles and phenomena. It is driven by curiosity and the desire to explore the underlying mechanisms of natural phenomena without any immediate practical application in mind. Researchers conducting basic research often seek to uncover new knowledge and contribute to the theoretical foundation of a field. This type of research serves as the building blocks for applied research and often involves theoretical frameworks, hypothesis testing, and exploration of new scientific frontiers.
Applied Research
Applied research focuses on utilizing existing scientific knowledge to address specific practical problems or develop new technologies and products. Unlike basic research, applied research is directly aimed at solving real-world issues and improving existing processes or products. It involves the application of scientific findings to develop innovative solutions, enhance efficiency, and meet practical needs in various industries and sectors. Applied research often encompasses fields such as engineering, medicine, agriculture, and technology, with a primary goal of delivering tangible and practical outcomes.
Experimental Research
Experimental research involves the systematic and controlled investigation of phenomena through carefully designed experiments. This type of research is characterized by the manipulation of variables to observe and analyze their effects on the subject of study. Experimental research follows a structured approach, where researchers formulate hypotheses, design experiments, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on empirical evidence. It is widely used in natural and social sciences to test causal relationships, validate theories, and generate empirical knowledge through rigorous experimentation.
Descriptive Research
Descriptive research focuses on describing the characteristics, behaviors, and attributes of a particular phenomenon or population without altering or influencing the subject of study. It involves the collection and analysis of data to provide a comprehensive overview or snapshot of the observed phenomena. Descriptive research methods include surveys, observational studies, case studies, and correlational studies, aiming to capture and present detailed information about the studied subjects. This type of research is valuable for establishing patterns, identifying trends, and gaining insights into specific phenomena.
Explanatory Research
Explanatory research seeks to elucidate the underlying causes and relationships between different variables or phenomena. It aims to uncover the reasons behind observed patterns or behaviors, providing a deeper understanding of the factors influencing a particular phenomenon. Researchers conducting explanatory research often employ analytical and inferential methods to establish connections, identify causal relationships, and offer explanations for complex phenomena. This type of research contributes to theoretical frameworks, model building, and the advancement of knowledge in diverse fields by unraveling the underlying mechanisms governing observed phenomena.
Steps In Scientific Research
Scientific research is a systematic process that involves various steps to ensure accurate and reliable results. These steps are crucial in understanding and solving complex problems in the scientific field. In this section, we will explore the different steps involved in scientific research, from identifying the research problem to drawing conclusions.
Identifying The Research Problem
Before starting any scientific research, it is essential to identify the research problem. This step involves understanding the gaps in existing knowledge and formulating a question that needs to be answered. The research problem sets the foundation for the entire study and guides the researcher in the subsequent steps.
Formulating Hypothesis
Once the research problem is identified, the next step is to formulate a hypothesis. A hypothesis is a tentative explanation or prediction based on existing knowledge or theories. It serves as a guide for the research and helps in testing the validity of the proposed explanation. The hypothesis can be either null or alternative, depending on the expected outcome of the research.
Designing The Research
After formulating the hypothesis, it is important to design the research study. This step involves determining the research design, selecting the sample size, and choosing the appropriate research methods and instruments. The research design should be carefully planned to ensure the collection of reliable and valid data.
Collecting Data
Once the research design is finalized, the next step is to collect data. This can be done through various methods such as surveys, experiments, observations, or interviews. The data collected should be relevant to the research question and should be collected in a systematic and unbiased manner. It is important to ensure the reliability and validity of the data collected.
Analyzing Data
After collecting the data, the next step is to analyze it. This involves organizing, summarizing, and interpreting the data using statistical techniques or other analytical methods. The data analysis helps in identifying patterns, relationships, and trends in the data and helps in answering the research question or testing the hypothesis.
Drawing Conclusion
The final step in scientific research is drawing conclusions based on the analysis of the data. This involves interpreting the results and determining whether they support or refute the hypothesis. The conclusions should be based on the evidence gathered and should be stated clearly and objectively. It is important to acknowledge the limitations of the study and suggest areas for further research.
Research Design
Introduction paragraph about Basics Of Scientific Research: What, How, And All About and Research Design…
Qualitative Research Design
Qualitative research design is a method used in scientific research that aims to explore and understand phenomena in-depth. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research emphasizes subjective experiences, perspectives, and meanings. It involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data, such as interviews, observations, and textual materials, to gain insights into the complexities and nuances of a research topic.
Here are some key features of qualitative research design:
- Focuses on understanding the “why” and “how” of a research topic
- Uses open-ended questions and flexible data collection methods
- Emphasizes context and the subjective experiences of participants
- Relies on the researcher’s interpretations and reflexivity
- Utilizes techniques like thematic analysis, content analysis, and grounded theory
Quantitative Research Design
Quantitative research design, on the other hand, is a method used to gather and analyze numerical data to examine relationships, patterns, and trends. It focuses on objective measurements and statistical analysis to draw conclusions and make generalizations about a population. This type of research design is often used in experiments, surveys, and statistical modeling.
Here are some key features of quantitative research design:
- Uses structured data collection methods, such as questionnaires and experiments
- Relies on statistical analysis to test hypotheses and draw conclusions
- Focuses on measurable variables and numerical data
- Seeks to establish cause-and-effect relationships
- Allows for generalization to a larger population
Mixed Research Design
Mixed research design, as the name suggests, combines elements of both qualitative and quantitative research. It integrates the strengths of both approaches to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a research topic. In a mixed research design, researchers collect and analyze both numerical and non-numerical data to gain a deeper insight into the phenomenon being studied.
Here are some key features of mixed research design:
- Uses a combination of qualitative and quantitative data collection methods
- Allows for triangulation of data to enhance validity
- Provides a more comprehensive understanding of the research topic
- Can support the exploration of relationships and the testing of hypotheses
- Offers flexibility in the research process
Data Collection Methods
Scientific research is a structured intellectual process that aims to solve problems in an organized scientific way. It involves various methods and techniques to collect, analyze, and interpret data to arrive at meaningful conclusions. One of the most crucial steps in scientific research is data collection, which involves gathering information through various methods and techniques. In this blog post, we will discuss the various data collection methods used in scientific research, including survey method, interview method, observation method, and experiment method.
Survey Method
The survey method is a popular data collection technique used in scientific research. It involves gathering data from a sample of individuals through a questionnaire or survey. Surveys can be conducted through various mediums, including online, phone, or in-person. This method is particularly useful in gathering quantitative data, such as demographic information, opinions, and attitudes. Here are some advantages and disadvantages of the survey method:
- Advantages:
- Easy to administer and collect data from a large sample size
- Cost-effective compared to other data collection methods
- Provides standardized data that is easy to analyze
- Disadvantages:
- May suffer from response bias, where respondents may not answer truthfully or may not answer at all
- May not be suitable for gathering qualitative data, such as detailed opinions or experiences
- May not accurately represent the population being studied if the sample size is not representative
Interview Method
The interview method involves gathering data through one-on-one conversations with individuals. This method is useful in gathering in-depth qualitative data, such as opinions, experiences, and perceptions. Interviews can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured, and can be conducted in person or over the phone. Here are some advantages and disadvantages of the interview method:
- Advantages:
- Allows for in-depth exploration of topics and issues
- Provides detailed qualitative data that is rich and nuanced
- Can clarify responses and probe for further information
- Disadvantages:
- Can be time-consuming and expensive compared to other data collection methods
- May suffer from interviewer bias, where the interviewer may influence the responses of the interviewee
- May not be suitable for gathering quantitative data, such as demographic information
Observation Method
The observation method involves gathering data by observing individuals or phenomena in their natural setting. This method is useful in gathering qualitative and quantitative data, such as behaviors, interactions, and frequencies. Observations can be structured or unstructured, and can be conducted overtly or covertly. Here are some advantages and disadvantages of the observation method:
- Advantages:
- Provides firsthand and objective data that is not influenced by self-report bias
- Allows for the observation of behaviors and interactions in their natural setting
- Can gather both qualitative and quantitative data
- Disadvantages:
- Can be time-consuming and expensive compared to other data collection methods
- May suffer from observer bias, where the observer may interpret the data differently
- May not be suitable for gathering detailed opinions or experiences
Experiment Method
The experiment method involves gathering data by manipulating variables in a controlled environment to test a hypothesis. This method is useful in gathering quantitative data and establishing cause-and-effect relationships. Experiments can be conducted in a laboratory or field setting and can involve various designs, such as randomized controlled trials or quasi-experiments. Here are some advantages and disadvantages of the experiment method:
- Advantages:
- Allows for the establishment of cause-and-effect relationships
- Can control for extraneous variables that may influence the results
- Provides quantitative data that is easy to analyze
- Disadvantages:
- Can be time-consuming and expensive compared to other data collection methods
- May not be suitable for gathering qualitative data, such as opinions or experiences
- May not accurately represent the real-world setting
Credit: www.sciencebuddies.org
Data Analysis Techniques
Scientific research is a crucial tool used to answer questions and solve problems by systematically collecting and analyzing data. Data analysis techniques are used to interpret the results of a scientific study and draw conclusions based on the evidence gathered. In this article, we will explore the basics of data analysis techniques used in scientific research, including descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and qualitative data analysis.
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics is the process of summarizing and describing the main features of a dataset. It involves analyzing the data and presenting it in a way that is easy to understand. Descriptive statistics provide information about the central tendency, variability, and distribution of data. Some common methods used in descriptive statistics include:
- Measures of central tendency: Mean, median, and mode
- Measures of variability: Range, variance, and standard deviation
- Frequency distributions: Histograms, bar charts, and pie charts
Descriptive statistics are useful for providing a general overview of the data and can help identify any trends or patterns in the data.
Inferential Statistics
Inferential statistics is the process of making predictions about a larger population based on a sample of data. It involves using probability theory to determine the likelihood that the results obtained from a sample are representative of the entire population. Some common methods used in inferential statistics include:
- Hypothesis testing: A statistical test used to determine if there is a significant difference between two groups
- Confidence intervals: A range of values that is likely to contain the true population parameter with a specified level of confidence
- Regression analysis: A statistical method used to determine the relationship between two or more variables
Inferential statistics are useful for making predictions and generalizations about a larger population based on a sample of data. It allows researchers to draw conclusions and make decisions based on the evidence gathered.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data analysis is the process of analyzing non-numerical data such as text, images, and audio recordings. It involves identifying patterns and themes in the data and interpreting the meaning behind them. Qualitative data analysis is often used in social sciences and humanities research. Some common methods used in qualitative data analysis include:
- Content analysis: A method used to analyze written or visual material to identify patterns and themes
- Grounded theory: A method used to develop a theory based on the data collected
- Thematic analysis: A method used to identify and analyze themes in qualitative data
Qualitative data analysis is useful for understanding complex social phenomena and gaining insight into people’s experiences and perspectives.
Ethical Issues In Scientific Research
Introduction paragraph about Basics Of Scientific Research: What, How, And All About and Ethical Issues in Scientific Research…
Informed Consent
When conducting scientific research, obtaining informed consent from participants is crucial. Informed consent ensures that participants are fully aware of the nature of the study, its purpose, potential risks and benefits, and their rights as participants. It is essential to explain the study in a way that is easily understandable, avoiding technical jargon and using plain language. Participants should be given the opportunity to ask questions and have them answered satisfactorily before providing their consent.
Key aspects of informed consent include:
- Clearly explaining the purpose of the study and what will be expected of participants.
- Providing information about any potential risks or discomfort that participants may experience.
- Informing participants of their right to withdraw from the study at any time without any negative consequences.
- Ensuring that participants are aware of the confidentiality measures that will be taken to protect their identity and personal information.
Confidentiality
Confidentiality is a critical ethical consideration in scientific research. Researchers have a responsibility to protect the privacy and personal information of participants. This includes ensuring that data collected during the study is kept secure and only accessible to authorized personnel. Participants should be assured that their identities will be kept confidential and that their information will be used solely for the purposes of the study.
Measures that can be taken to maintain confidentiality include:
- Removing any identifying information from data collected, using codes or pseudonyms instead.
- Storing data in secure databases or encrypted files.
- Limiting access to data to only those individuals involved in the research.
- Obtaining informed consent from participants regarding the use and storage of their data.
Privacy
Respecting the privacy of participants is another ethical consideration in scientific research. Researchers should ensure that participants’ privacy is protected throughout the study and that their personal information is not disclosed without their explicit consent. This includes safeguarding any sensitive or confidential information shared by participants during the research process.
Ways to uphold privacy in scientific research include:
- Using secure communication channels for data collection and participant interaction.
- Obtaining explicit permission from participants before sharing any information that could potentially identify them.
- Adhering to relevant data protection regulations and guidelines.
Plagiarism
Plagiarism is a serious ethical violation in scientific research. It involves presenting someone else’s work or ideas as one’s own, without giving proper credit. Plagiarism undermines the integrity of the research process and can have severe consequences for the researcher’s reputation and career.
To avoid plagiarism, researchers should:
- Cite all sources used in their research, including both direct quotes and paraphrased information.
- Use proper referencing formats, such as APA or MLA, as required by their field.
- Clearly distinguish their own ideas and contributions from those of others.
Research Fraud
Research fraud involves the fabrication, falsification, or plagiarism of data in scientific research. It is a grave ethical violation that undermines the integrity of the scientific community and can have far-reaching consequences. Research fraud not only damages the credibility of the researcher but also hinders scientific progress and can lead to wasted resources.
Preventing research fraud requires:
- Conducting research with honesty and integrity, following ethical guidelines and best practices.
- Keeping accurate and detailed records of research procedures and data.
- Engaging in peer review and collaboration to ensure the validity of research findings.
- Reporting any suspected instances of research fraud to the appropriate authorities or institutions.
Future Of Scientific Research
Scientific research has always been at the forefront of advancements and discoveries, pushing the boundaries of knowledge and understanding. As we move into the future, the field of scientific research is poised to evolve and expand even further, opening up new avenues of exploration and discovery. In this section, we will explore the emerging fields of research, the new technologies that are revolutionizing the way research is conducted, and the impact of scientific research on society.
Emerging Fields Of Research
The world of scientific research is constantly evolving, with new fields of study emerging and gaining momentum. These emerging fields are often interdisciplinary in nature, combining different scientific disciplines to tackle complex problems and uncover new insights. Some of the emerging fields of research include:
- Biotechnology and genetic engineering
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning
- Nanotechnology
- Climate change and environmental science
- Neuroscience and brain research
These emerging fields hold great potential for scientific breakthroughs and have the power to shape the future in profound ways. Researchers in these fields are pushing the boundaries of what is known and opening up new possibilities for innovation and discovery.
New Technologies For Research
The advancement of technology has revolutionized the way scientific research is conducted. New technologies have made it possible to collect, analyze, and interpret data in ways that were previously unimaginable. Some of the new technologies that are transforming scientific research include:
- High-performance computing and big data analytics
- Genome sequencing and gene editing technologies
- Virtual reality and augmented reality
- Remote sensing and satellite imaging
- Robotics and automation
These technologies not only enhance the efficiency and accuracy of research but also enable scientists to explore new frontiers and tackle complex problems with greater precision. They are instrumental in driving scientific progress and opening up new possibilities for exploration and discovery.
Impact Of Scientific Research On Society
Scientific research has a profound impact on society, shaping our understanding of the world and driving innovation and progress. Some of the key impacts of scientific research on society include:
- Medical advancements and improved healthcare
- Technological innovations and improved quality of life
- Environmental conservation and sustainable development
- Enhanced understanding of the natural world and the universe
- Social and cultural transformations
Scientific research has the power to address pressing societal challenges, improve living conditions, and create a better future for all. It is through scientific research that we gain knowledge, develop new technologies, and make informed decisions that shape our world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Basic Concept Of Scientific Research?
The basic concept of scientific research involves systematic study and experimentation to discover new knowledge and understand natural phenomena. It aims to gather empirical evidence through observation and analysis. Scientific research is vital for advancements in various fields and contributes to societal progress and problem-solving.
What Are The Basic Steps Of Scientific Research?
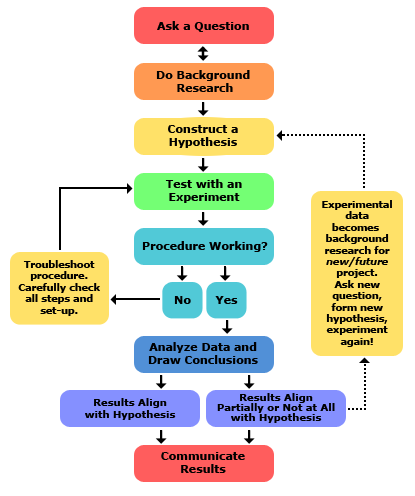
The basic steps of scientific research include asking a purposeful question, conducting background research, forming a hypothesis, designing and performing experiments, analyzing data, and drawing conclusions. These steps drive progress, contribute to development, and solve problems in an organized manner.
What Is The Basic Process Of Science Research?
The basic process of scientific research involves asking a question, conducting background research, forming a hypothesis, experimenting, analyzing data, and drawing conclusions. This structured process drives progress and contributes to advancements in various fields.
What Are The Basic Principles Of Scientific Research?
The basic principles of scientific research include empirical research, which is based on observable and measurable evidence, and the use of systematic and organized methods to solve problems. Scientific research is important for progress and development in all fields and contributes to economic, political, and social progress.
It also leads to advancements in various areas such as medicine and communication. Overall, scientific research is essential for the advancement of knowledge and understanding for the benefit of humanity.
Conclusion
Scientific research is a vital component of progress and development in various fields. It is an intellectual process that allows us to solve problems systematically and contribute to society’s well-being. Through research, we gain a deeper understanding of the natural world and make advancements in medicine, communication, and other areas.
Scientific research plays a crucial role in times of crises and helps nations strive for power and technological superiority. Ultimately, it is through research that we expand our knowledge and improve the lives of people worldwide.



